PATHAS
PATHAS. Networked fault-tolerant and PATH tracking-based driving Automation System to enhance vehicle stability, comfort and safety under uncertainties and external disturbances
Grant [PID2022-136468OB-I00] funded by MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033 and, by “ERDF A way of making Europe”.
PUBLICATIONS
- Enhanced Metamodeling Strategy for Uncertainty Quantification and Reliability Verification in Heterogeneous Connected and Automated Vehicle Platoon Control Models. Ramón Gutiérrez-Moizant, Fernando Viadero-Monasterio, Maria Jesus Lopez Boada, Beatriz Lopez Boada. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 112183. January 2026.doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2025.112183.
- Low-Cost Vehicle Rebalancing Control for an Autonomous Mobility on Demand System. Fernando Viadero-Monasterio, Miguel Meléndez-Useros, Hui Zhang, Beatriz L. Boada and Maria Jesus L. Boada.Journal of the Franklin Institute,108333, 2025. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2025.108333.
- Active steering fault diagnosis via integrated LSTM-based sensor detection and robust actuator fault estimation. M. Meléndez-Useros, M. Meléndez-Useros, M. Jiménez-Salas and MJL. Boada. Reliability Engineering & System Safety. Vol. 265, Part A, January 2026, 111573. doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2025.111573
- Robust Adaptive Control of Heterogeneous Vehicle Platoons in the Presence of Network Disconnections With a Novel String Stability Guarantee. F. Viadero-Monasterio, M. Meléndez-Useros, M. Jiménez-Salas and B. L. Boada. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2025. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2025.3578936
- Key influencing factors in vehicle platoons: a systematic study and review. Viadero-Monasterio, F., Meléndez-Useros, M., Jiménez-Salas, M., López Boada, B., & Jesus Lopez Boada, M. Evolving Systems, 16(4), 1-13. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s12530-025-09746-1.
- Reliability Analysis of Vehicle Semi-Active Suspension Systems Under Parameter Uncertainties in Magnetorheological Dampers, Ramón Gutiérrez-Moizant, Andrés Ricardo Valdez, Maria Jesus Lopez Boada, Beatriz Lopez Boada, María Ramírez-Berasategui, Results in Engineering, 106301. 2025. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2025.106301
- Motion Planning and Robust Output-Feedback Trajectory Tracking Control for Multiple Intelligent and Connected Vehicles in Unsignalized Intersections. Fernando Viadero-Monasterio; Miguel Meléndez-Useros; Nianhua Zhang; Hui Zhang; Beatriz L. Boada; Maria Jesus L. Boada. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2025.3586769
- Signalized Traffic Management Optimizing Energy Efficiency Under Driver Preferences for Vehicles With Heterogeneous Powertrains.Fernando Viadero-Monasterio; Miguel Meléndez-Useros; Hui Zhang; Beatriz L. Boada; Maria Jesus L. Boada. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics. 2025. .doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2025.3569967
- Avoiding Lyapunov-Krasovskii Functionals: Simple Nonlinear Sampled–Data Control of a Semi-Active Suspension with Magnetorheological Dampers. Fernando Viadero-Monasterio; Miguel Meléndez-Useros; Manuel Jiménez-Salas; María Jesús López Boada. Machines, 13, 512. 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13060512.
- Fault-Tolerant Robust Output-Feedback Control of a Vehicle Platoon Considering Measurement Noise and Road Disturbances. Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Meléndez-Useros, M.; Jiménez-Salas, M.; López Boada, M. J. IET Intelligent Transport Systems. 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.1049/itr2.7000.7
- Static Output-Feedback Path-Tracking Controller Tolerant to Steering Actuator Faults for Distributed Driven Electric Vehicles. Meléndez-Useros, M., Viadero-Monasterio, F., Jiménez-Salas, M., and López Boada, M. J. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16010040
- Static Output Feedback Control for Vehicle Platoons with Robustness to Mass Uncertainty. F. Viadero-Monasterio, R. Gutiérrez-Moizant, M. Meléndez-Useros, M.J.L. Boada. Electronics. 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14010139.
- Enhancing Driving Safety Through Robust Static Output-Feedback Path Tracking and Emergency Braking Control Under Network-Induced Delays. F. Viadero-Monasterio, M. Jimenez-Salas, M. Melendez-Useros, H. Zhang, B.L. Boada and M.J.L. Boada. The 9th 2025 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD), 1-3 July 2025, Barcelona, Spain.
- Useros, M. M., Salas, M. J., Monasterio, F. V., Tajuelo, J. M. C., Boada, B. L., & Boada, M. J. L. (2025, May). Diseño de un Controlador Tolerante a Fallos en la Dirección mediante Vectorización de Torque para Vehículos Eléctricos. In Anales de Ingeniería Mecánica (Vol. 1, No. 24). doi: https://doi.org/10.63450/aim.1.122.2025.
- Moizant, R. A. G., Monasterio, F. V., Boada, B. L., & Boada, M. J. L. (2025). Estrategia Avanzada de Modelo Subrogado para la Cuantificación de la Incertidumbre en Pelotones de Vehículos Heterogéneos. In XXV Congreso Nacional de Ingeniería Mecánica: libro de actas (p. 112). Asociación Española de Ingeniería Mecánica. doi: https://doi.org/10.63450/aim.1.136.2025.
- Monasterio, F. V., Useros, M. M., Salas, M. J., Moizant, R. A. G., Ramos, D. G. P., Boada, M. J. L., & Boada, B. L. (2025, May). Mejora de la Seguridad y el Confort en Vehículos Autónomos mediante Control Combinado de Seguimiento de Trayectoria y Balanceo. In Anales de Ingeniería Mecánica (Vol. 1, No. 24). doi: https://doi.org/10.63450/aim.1.124.2025.
- Salas, M. J., Useros, M. M., Viadero-Monasterio, F., Boada, M. J. L., & Boada, B. L. (2025, May). Control de seguimiento de trayectoria durante maniobras evasivas de un vehículo usando MPC-offline y vectorización de par. In Anales de Ingeniería Mecánica (Vol. 1, No. 24). doi: https://doi.org/10.63450/aim.1.133.2025.
- Robust Static Output Feedback Control of a Semi-Active Vehicle Suspension Based on Magnetorheological Dampers. F. Viadero-Monasterio, M. Meléndez-Useros, M. Jiménez-Salas, B.L. Boada. Applied Sciences. 2024. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/app142210336.
- Robust Adaptive Heterogeneous Vehicle Platoon Control based on Disturbances Estimation and Compensation. F. Viadero-Monasterio, M. Meléndez-Useros, M. Jimenez-Salas, B.L. Boada. IEEE Access. 2024. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3428341.
- Robust Output Feedback Control for Heterogeneous Autonomous Vehicle Platoons. Fernando Viadero-Monasterio, Manuel Jiménez-Salas, Miguel Meléndez-Useros, María Jesús López Boada. Dyna Ingeniería e Industria. 2024. doi: https://doi.org/10.52152/D11088.
- Manuel Jimenez-Salas, Basilio Lenzo, Miguel Melendez-Useros, Fernando Viadero-Monasterio, María Jesus Lopez Boada, Beatriz Lopez Boada.Combined lateral and longitudinal energy efficient MPC control for vehicle path tracking. Mechanism and Machine Theory Symposium. Guimaraes. Portugal. 26-28 June. 2024
- Miguel Melendez-Useros, Manuel Jimenez-Salas, Fernando Viadero-Monasterio, Beatriz Lopez Boada, María Jesus Lopez Boada. Robust active suspension control tolerant to sensor faults. Mechanism and Machine Theory Symposium. Guimaraes. Portugal. 26-28 June. 2024
- Fernando Viadero-Monasterio, Miguel Melendez-Useros, Manuel Jimenez-Salas,, Beatriz Lopez Boada, María Jesus Lopez Boada. Robust-semiactive suspension control using magnetorheological dampoers. Mechanism and Machine Theory Symposium. Guimaraes. Portugal. 26-28 June. 2024
- Novel Methodology for Integrated Actuator and Sensors Fault Detection and Estimation in an Active Suspension System. M. Melendez-Useros, M. Jimenez-Salas, F. Viadero-Monasterio and M.J.L. Boada. IEEE Transactions on Reliability. 2024. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TR.2024.3389290.
- Viadero-Monasterio, F.; Meléndez, M; Jiménez-Salas, M.; L. Boada, B. and L. Boada, M. J. What are the most influential factors in a Vehicle Platoon?. IEEE International Conference on Evolving and Adaptive Intelligent Systems. Madrid, Spain. 23-24 May, 2024.
- Simultaneous Estimation of Vehicle Sideslip and Roll Angles Using an Event-Triggered-Based IoT Architecture. Viadero-Monasterio, F.; García, J.; Meléndez-Useros, M.; Jiménez-Salas, M.; Boada, B.L.; López Boada, M.J. Machines 2024, 12, 53. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/machines12010053
- Event-Triggered Robust Path Tracking Control Considering Roll Stability Under Network-Induced Delays for Autonomous Vehicles. F. Viadero-Monasterio, A-T. Nguyen, J. Lauber, M.J.L. Boada and B.L. Boada. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2023. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3321415
- Novel Bayesian Inference-Based Approach for the Uncertainty Characterization of Zhang’s Camera Calibration Method. R. Gutierrez-Moizant, M.J.L. Boada, M. Ramirez-Berasategui and A. Al-Kaff. Sensors. 23(18), 7903. 2023. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187903.
- Viadero-Monasterio, F., Jiménez-Salas, M., Meléndez-Useros, M., L. Boada, B. and L. Boada, M. J., "Event-triggered fault-tolerant control for vehicle rollover avoidance based on an active suspension with robustness against disturbances and communication delays", 16th IFToMM World Congress, 2023
- Viadero-Monasterio, F., Jiménez-Salas, M., Meléndez, M., L. Boada, B. and L. Boada, M. J., "Diseño de un sistema de control en pelotón heterogéneo para vehículos automatizados", XXIV Congreso Nacional de Ingeniería Mecánica, 2023
GENERAL OBJECTIVE
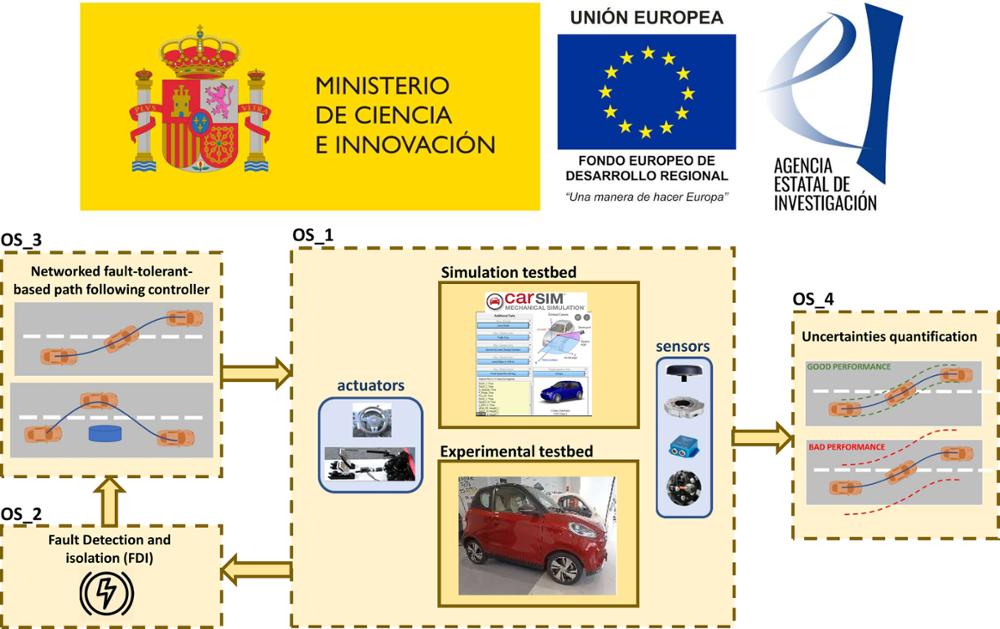
The general objective of the project is the design of an in-vehicle path-tracking-based driving automation system to enhance vehicle stability, comfort and safety under uncertainties/disturbances and sensor/actuator faults using dynamic sensors. This project has a strong interdisciplinary character and needs to be approached from the following thematic areas: Area 11. PIN / Industrial production, civil engineering and engineering for society in the field of Mechanical (fault detections, uncertainties quantification, vehicle dynamics), including analytical, numerical and experimental methods and Area 13. EYT / Energy and transportation to generate new knowledge that allows the development of innovative techniques for design of systems of transport in the automotive mode (path tracking system for an ADS).
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
The specific objectives coming from the defined general objective are:
- OS_1. Design of a vehicle testbed to prove the performance of the designed path-tracking-based system.
- OS_2. Design of fault detection and isolation (FDI) system for a path tracking controller.
- OS_3: Design of a fault-tolerant and networked-based path tracking controller under uncertainties and external disturbances.
- OS_4: Design of a tool for path tracking sensitivity analysis and confidence regions calculation.
EXPECTED IMPACT ON THE GENERATION OF SCIENTIFIC-TECHNICAL KNOWLEDGE
This project will have a high scientific-technical impact, since it is intended to design a novel networked-based fault-tolerant path tracking system under disturbances and uncertainties to enhance vehicle stability, comfort and safety, especially in critical driving and traffic situations. This proposal will contribute to the Strategic Action AE5: Climate, Energy and Mobility in the search for new solutions and the advancement of knowledge in automated mobility. The evolution and consolidation of existing and proven automatic driving systems, such as the one considered in this proposal, to form automated and connected vehicles will further expand the positive contribution towards enhancing road safety and smart mobility. The designing of a path tracking controller is one of the most fundamental concerns for autonomous vehicles.
From the economical point of view, the economic effects of the coming autonomous-driving technologies will be very remarkable. One of the first analyses estimated the economic impact of autonomous vehicles up to $1.9 trillion per year by 2025. Recent research finds that autonomous driving technology will enable a new economy worth $7 trillion in 2050. It should be noted that Spain has an important vehicular industry that can be interested in this type of research. The active promotion of autonomous driving systems, as this project aims, will contribute to further strengthen the Spanish automotive industry’s role as a leading innovator and lend a further boost to adjacent growth markets for information and communications technologies and innovative digital services.
Another expected impact of the project is to contribute to improve the safety in road transport with the associated economic consequences. According to ASIRT (Association for Safe International Road Travel), approximately 1,3 million people die annually in car accidents and around 20-50 million suffer serious injuries. These accidents cause a global cost of 518 billion USD, which is between the 1-2% of GDP of a country. The accidents have a high socioeconomic impact related to hospital expenses, the material losses and the loss of the production of the injured people. For all these reasons, the requested project will have high impact at European, National and Autonomous Community levels.
From the social point of view, autonomous vehicles will contribute to moving towards sustainable and safe mobility. The European Commission adopted in 2019 the EU Road Safety Policy Framework 2021-2030 which aims to halve the number of deaths and serious injuries on European roads by 2030, as a milestone on the way to "Vision Zero"-zero deaths and serious injuries by 2050. Additionally, autonomous vehicles can provide an excellent alternative for the mobility of disabled or elderly people who are incapable of driving conventional vehicles.
Finally, the project results will contribute to support the acquisition of new skills, retain and reskill the workforce in the sector through the new skills agenda for Europe and evaluate the options for facilitating the transition to automation in the road sector.
This project brings together some of the main challenges that exist today: innovation, digitalization and sustainability to generate a positive impact on the economic growth of the EU. It is also aligned with the achievement of certain Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) proposed by the United Nations in its SDG2030 framework, with special emphasis on the following: 3. Good Health and Well-Being: contributing to improve the road safety reducing the number of deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents. 9. Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure: Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors designing of a smart vehicular system with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all. And 11. Sustainable Cities and Communities: provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, people with disabilities and the elderly.




SOCIAL AND ECONOMIC IMPACT